For drinking applications or hygienic media for consumption, it is essential that the water does not get contaminated. Depending on the application, the water can come into contact with pipes, hoses, fittings, and valves. These products that come into contact with water must be specially certified, designed, produced, and implemented to ensure that they do not cause any health hazards for the consumer. Throughout the process line, from the inlet to the outlet, chemical contaminants, like lead, may be present in the plumbing, minerals, temperature, and flow of the potable water may contribute to corrosion, leading to contamination into the drinking water supply. Thus, it is crucial to install the right product, to have the right material for the components, and to verify that the components meets the drinking water certifications and regulations.

Different Global Certifications
There are several guidelines and certifications worldwide that monitor and control the quality of components that come into contact with drinking water. Below are some of the more commonly known certifications for drinking water valves:
WRAS approvals demonstrates the compliance of material and water fittings in contact with the public mains water supply, with the requirements of Water Supply Regulations in UK and Scottish byelaws.

WaterMark certification scheme is a mandatory certification for plumbing and drainage products for sale in Australia and New Zealand.
The VDE mark certifies electro-technical products including products according to the Product Safety Act (ProdSG) and medical products according to the Medical Product Act (MPG). According to VDE/EN/IEC standards, other technical specifications as well as possible provisions of law will respect to safety and health requirements.
KTW is a guideline on the hygienic assessment of organic materials such as plastics and silicones in contact with drinking water, and W270 describes a method for the assessment of microbial growth on non-metallic materials in contact with drinking water. The DVGW (Deutscher Verein des Gas- und Wasserfaches) provides the required testing and certification for these products.

The criteria is for certification (attestation of conformity) of products in contact with drinking water according to the evaluation criteria which the German Environment Agency has set up a recommendation.

The Kiwa watermark provides certification for products that come into contact with drinking water for the Dutch market. Its guidelines include all the market and government requirements. Thus, producers and suppliers only have to deal with one set of requirements.

NSF/ANSI 61 is a set of standards in North America, which establishes the requirements and guidelines for equipment that comes into contact with drinking water or products that support production of drinking water.
The ACS is a material safety approval mandatory for all materials and products in contact with drinking water in France.

Valves for Drinking Water Applications
Depending upon the application, different type of valves should be used to properly control the flow. The four commonly used valve types are discussed below:
Solenoid Valve
A water solenoid valve is used in applications that require automatic flow control. Depending on the design, the valve can be normally-closed or normally-open. They are controlled by an electrical signal that can be done remotely and automatically to accurately and reliably control water flow. Solenoid valves are typically quick acting, so for water applications a solenoid valve with an adjustable closing timer are used to prevent a water hammer. Below are some of the drinking water solenoid valves Flu-Tech offers:
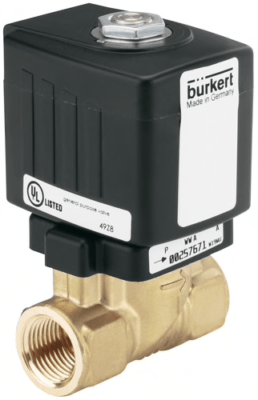
Burkert – Type 6213 2/2-Way N/C Servo Coupled Solenoid Valve
- 0 to 145 PSI
- 3/8″ to 1″ NPT
- IP 65 with Cable Plug
- NSF 61/372 Approved
- Class F or Class H Coils
- Water Hammer-Free (Low Noise)
- Spring Coupled Diaphragm System
- EPDM Seals with Stainless Steel or Lead-Free Brass Housing
- Slip Over Coil Technology; 100% Continuous Rating Duty Cycle
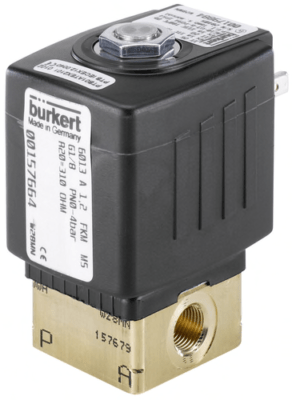
Burkert – Type 6013 2/2-Way Direct-Acting Plunger Valve
- Up to 362 PSI
- 1/8″ or 1/4″ NPT
- IP 65 Cable Plug
- 2-Way N/C or NO
- NSF 61/372 Approved
- Class F or Class H Coils
- EPDM Seals with Cable Plug with Stainless Steel Housing
- Slip Over Coil Technology; 100% Duty Cycle; High Cycling Rate

Burkert – Type 6011 2/2-Way N/C Direct-Acting Plunger Valve
- 1/8″ NPT
- Up to 164 PSI
- IP 65 with Cable Plug
- NSF 61/372 Approved
- Directing Acting Miniature Valve
- EPDM Seal with Stainless Steel Housing
- Slip Over Coil Technology; 100% Duty Cycle; High Cycle Rate
Ball Valves
A ball valve controls the flow with a rotary ball having a bore. When the bore is aligned in the same direction as the pipe, the valve is opened, allowing the water to flow through it. When the ball is rotated by 90 degrees, the bore is perpendicular to the flow path and the water flow is blocked. This rotation can be done manually with a lever, or with an actuator (electric or pneumatic). Ball valves provide reliable sealing and are typically used in residential application for main or branch line shut-off of domestic hot and cold water system.
Gate Valves
A gate valve, also known as a shut-off valve, is typically a manually controlled valve that is typically only used in the fully open or fully closed state. Therefore, it is not used as a control valve and using them as such may wear out the valve and cause inaccurate flow control. It is typically used in large diameter piping and high-pressure application. A gate valve can be used where water does not need shutting-off frequently, like in the main water pipelines to homes.
Check Valves
A check valve is a one-way valve which allows the water to flow in only one direction. Water flow in the desired direction opens the valve while any backflow forces it closed preventing any flow. For drinking water applications, a check valve is used to prevent the backflow from the outlet into the water source to prevent contaminants from entering the drinking water system. The check valve is also used on private well systems to keep the water in the pipes and keep the pump primed.
Valve Material
A valve’s housing and sealing material are a critical element when selecting the right valve for drinking water applications. These materials should be approved for use with drinking water. The following housing and sealing materials are the most commonly available options:
Housing Material
Brass is the more traditional choice of material for drinking water valves. It provides economical value and can perform within a wide temperature range. However, brass alloys often contain lead which is added to increase the machinability. Considering the hazardous effect of lead on human health, various regulations have been enforced to ensure lead-free drinking water. In North America, EPA limits the maximum lead content to 0.25% calculated across the wetted surface area. Manufacturers and contractors must calculate the wetted surface area and total lead content for drinking water system to determine the usability of the valve for drinking water purposes. Lead-free brass options are also available as replacements for traditional brass valves for drinking water application.

Composite or plastic materials are commonly used for commercial and residential applications. It is a lead-free alternative and saves the manufacturers from undertaking wetted average area calculations for lead contents. However, composite materials may be slightly more expensive than brass valves.

Stainless steel is another commonly used material for drinking water valve. They are lead-free and provide a broad range of options in terms of flow coefficient, sizing, temperature and pressure range. However, they are a more expensive material choice, but with no lead content, it is also a safe option.
Seal Material
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is the most commonly used material as a diaphragm, O-ring and/or seal in drinking water valves. It is suitable for drinking water, won’t contaminate it, and can withstand a temperature range from -18°C to +80°C (0°F to +176°F).

Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) is typically used as a seal material for temperature ranges above NBR’s capabilities. It can withstand a temperature range of -20°C to +139°C (-4°F to +282°F) and is therefore suitable for hot and cold water applications.
Reference: Burkert, Tameson, Kiwa, NFS

สำหรับข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม โปรดติดต่อเรา:
โทร: 02-384-6060 | ไลน์: @flutech.co.th | อีเมล: [email protected] | เฟสบุ๊ค: @flutech.co.th