International MACHINE Safety standards level
Type A
Basic Standards
Fundamental machine safety standards applicable to all machinery.
Type A standards deal with:
- Basic concepts
- Principle for design
- General aspects
Type B
Application Standards
Type B is divided into two categories – B1 and B2.
B1 – Specific safety aspects:
- Safety distances
- Surface temperature
- Noise
B2 – Safety related devices:
- Two-hand controls
- Interlocking devices
- Pressure sensitive devices
- Guards
Type C
Specific Machine Standards
Standards applicable to specific machinery.
- Vertical standards covering a single type of machine or group of machines
- Use A and B standards to create C standards

SAFETY STANDARDS FOLLOW SIMILAR FLOW AND HAVE SIMILAR CONTENT AROUND THE GLOBE
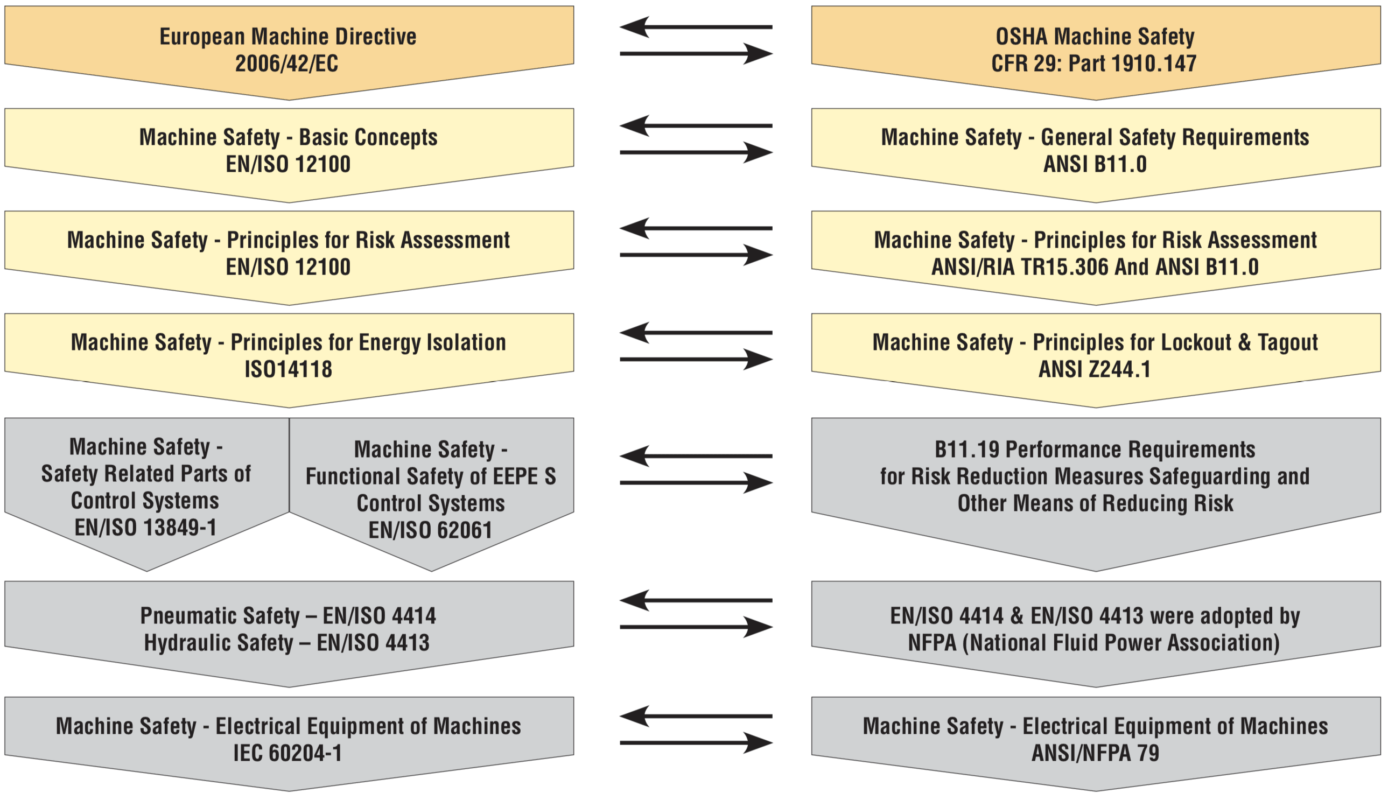
MACHINE SAFETY REQUIREMENTS
OSHA CFR 29
One of the “root causes” of workplace injuries, illnesses, and incidents is the failure to identify or recognize hazards that are present, or that could have been anticipated. A critical element of any effective safety and health program is a proactive, ongoing process to identify and assess such hazards.
Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC
The manufacturer of machinery or his authorized representative must ensure that a risk assessment is carried out in order to determine the health and safety requirements which apply to the machinery. The machinery must then be designed and constructed taking into account the results of the risk assessment.
International Standards ISO 4414:2010 & 4413:2010
When designing pneumatic and hydraulic systems for machinery, all intended operations and use of systems shall be considered. Risk assessment, e.g., in accordance with ISO 12100:2010, shall be carried out to determine the foreseeable risks associated with systems when they are used as intended. Reasonably foreseeable misuse shall not cause hazards. The risk identified shall be eliminated by design, and where this is not practicable, safeguards (first preference) or warnings (second preference) against such risk shall be incorporated, in accordance with the hierarchy established in ISO 12100, ISO 4414 & 4413.
MACHINE SAFETY DEVELOPMENT PROCESS
For more information regarding risk assessment and risk reduction, click here.
Examples of ROSS Machine Safety Products:
Inline Poppet Soft Start Valve
27 Series
- An EEZ-ON® valve is used in an air supply line to provide a gradual buildup of downstream air pressure
- Permits cylinders or other work elements to move slowly into their normal working positions before full line pressure is applied
- The time required to reach full line pressure is adjustable
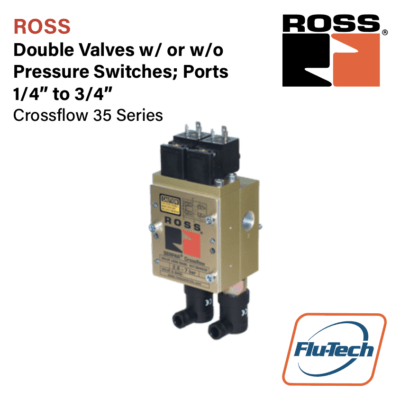
Double Valves w/ or w/o Pressure Switch, 1/4″ to 3/4″ Ports
Crossflow 35 Series
- Designed to enable users to comply with current safety regulations
- Can be integrated with external monitoring systems to provide for lockout and inhibiting further machine operation until the controls system is reset
- Default to de-energized position upon fault condition
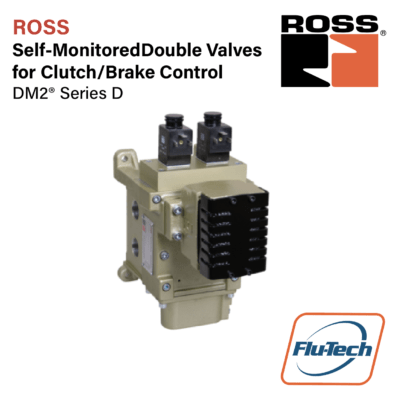
Self Monitored Double Valves for Clutch/Brake Control
DM2® Series D
- Highly contaminant tolerant poppet construction
- High flow, clog resistant silencers
- Provides redundancy, dynamic monitoring and memory for the mechanical press industry regarding the control of pneumatically controlled clutch and brake applications
- Base mounted
สำหรับข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม โปรดติดต่อเรา:
โทร: 02-384-6060 | ไลน์: @flutech.co.th | อีเมล: [email protected] | เฟสบุ๊ค: @flutech.co.th










